[ad_1]
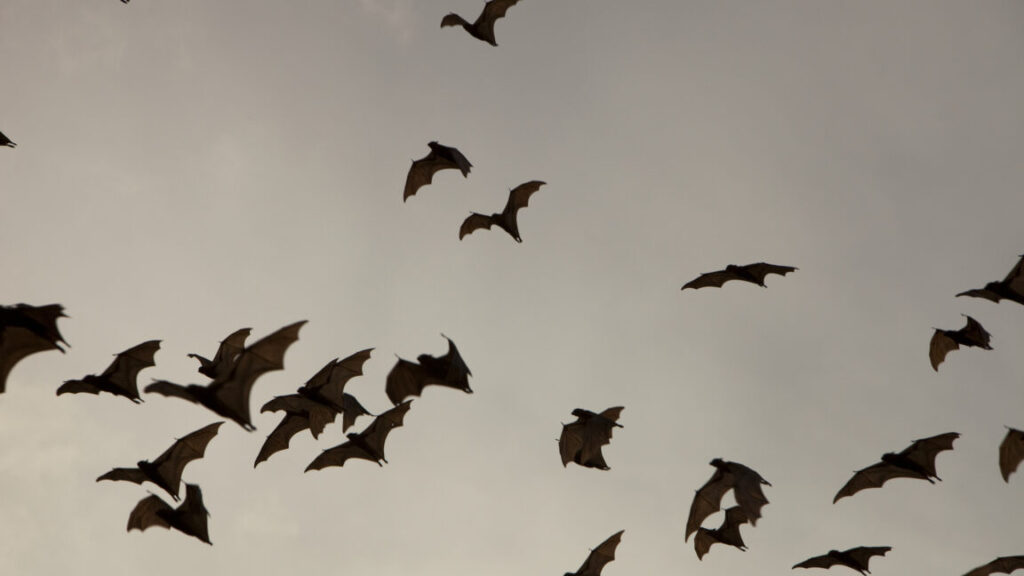
Bat maps
To evaluate the route each bat took to get back to the roost, the team used their simulations to measure the echoic entropy it experienced along the way. The field where the bats were released was a low echoic entropy area, so during those first few minutes when they were flying around they were likely just looking for some more distinct, higher entropy landmarks to figure out where they were. Once they were oriented, they started flying to the roost, but not in a straight line. They meandered a bit, and the groups with higher sensory deprivation tended to meander more.
The meandering, researchers suspect, was due to trouble the bats had with maintaining the steady path relying on echolocation alone. When they were detecting distinctive landmarks like a specific orchard, they corrected the course. Repeating the process eventually brought them to their roost.
But could this be landmark-based navigation? Or perhaps simple beaconing, where an animal locks onto something like a distant light and moves toward it?
The researchers argue in favor of cognitive acoustic maps. “I think if echolocation wasn’t such a limited sensory modality, we couldn’t reach a conclusion about the bats using cognitive acoustic maps,” Goldshtein says. The distance between landmarks the bats used to correct their flight path was significantly longer than echolocation’s sensing range. Yet they knew which direction the roost was relative to one landmark, even when the next landmark on the way was acoustically invisible. You can’t do that without having the area mapped.
“It would be really interesting to understand how other bats do that, to compare between species,” Goldshtein says. There are bats that fly over a thousand meters above the ground, so they simply can’t sense any landmarks using echolocation. Other species hunt over sea, which, as per this team’s simulations, would be just one huge low-entropy area. “We are just starting. That’s why I do not study only navigation but also housing, foraging, and other aspects of their behavior. I think we still don’t know enough about bats in general,” Goldshtein claims.
Science, 2024. DOI: 10.1126/science.adn6269
[ad_2]
Source link